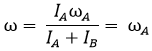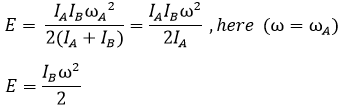Read:
What is a Clutch? - Types of Clutches
Consider a plate or
disc clutch
Let
I
A = mass moment inertia of rotors attached to shaft A
I
B = mass moment inertia of rotors attached to shaft B
ω
A = Angular speed of shat A before engagement
ω
B = Angular speed of shat B before engagement
ω = Common angular speed of shat A and Shaft B after engagement
According to the principle of conservation of momentum, Total momentum before clutch engage is equal to the total momentum of the clutch after clutch disc engagement.
IA ω
A + IB ω
B = (I
A + I
B)ω
Common angular speed after engagement of clutch pressure plate
Total Kinetic energy before
friction clutch engagement
Kinetic energy after clutch engagement
Put the value of ω into above equation,
Now the loss of energy during clutch engagement, E= E
1-E
2
Apply Different condition for above equation
Condition I - The rotor attached and hence the shaft B at rest ω
B = 0
Put these condition in equation (a), and equation (b) we get
Common angular speed after the clutch engagement,
Loss of kinetic energy
Condition II - If rotor B at rest (ω
B = 0) and I
B is very small when compared to I
A
Common angular speed after the clutch engagement,
Kinetic energy loss,
.png)