Injection Moulding Machine Working Principle and The Process
What is plastic injection moulding?
Injection moulding is one of the most commonly used processes to produce thermoplastic plastic parts. It is a cyclic process of mould filling followed by cooling and ejection. It is very economical in mass production. In fact, the feedstock need not be plastic; it can be plastic and non-plastic material. However, the machine should be configured to the feedstock material, and material must be plasticized before injection.
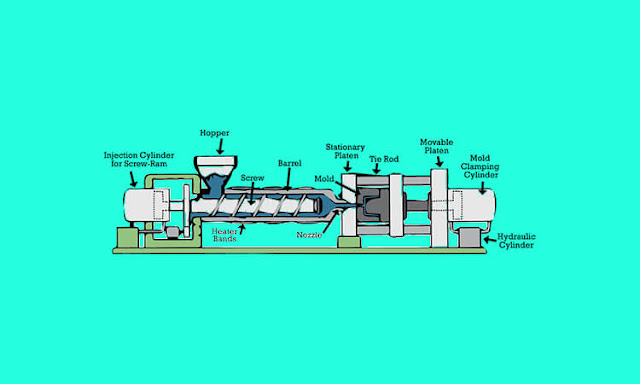
The following figure shows the schematic diagram of the industrial injection moulding machine. Two principal central units of injection moulding machines are the injection unit and clamping unit.
Injection moulding process
Injection moulding machines generally perform some essential functions.
Plasticizing: Heating and melting the material in the plasticator.
Injection: Inject the controlled volume of melted material into the closed mould.
After filling: Maintain the injected material under pressure in the mould for a specific time during solidification to prevent back flow of melt and compensate the decrease in volume during the solidification process.
🔗What is shrinkage /contraction allowance?
Cooling: Cool the melt until it is sufficiently rigid to be ejected.
Moulded part releasing: Complete the cycle by opening the mould and ejecting the part.
The material generally available as grains and pellets is first compressed in a high-pressure chamber and pushed into a heating chamber. The plastic pellet melts in homogeneous manner in the heating chamber. It is then injected through a nozzle into a clamped mould with a cavity of the desired shape with high pressure (500 - 1500 bar). The clamping unit holds the two units of moulds (fixed half and moving half) securely in proper alignment for the injection process. The item of the intricated shape formed in these mould cavities is then removed by opening the moulds.
The following methods are used to inject molten material into mould.
1) Reciprocating screw injection
2) Plunger injection
3) Two-stage injection - In the first stage, the material plasticizes, then a definite amount is transferred into the shot chamber by a reciprocating screw. In the second stage, the plunger injects the plasticized material into the mould from the shot chamber.
The reciprocating screw injection is the most common.
In an injection moulding machine, the mould and plasticized area are separated from each other. The temperature of the plasticizing area is high as the processing temperature. The solidification of molten plastic begins from the walls of the mould cavity. The mould area is kept cold enough to demoulding of the produced parts. After cooling, the mould is opened, and the product is removed by using an ejector mechanism.
🔗Injection moulding application advantages and limitations
What are the principal variables that control the moulding process?
The following are the principal variable that must be controlled in injection moulding.
- The temperature of plastic material.
- The temperature of the mould.
- Injection pressure.
- Quantity of plastic material that injected to mould.
- Injection speed.
- The plunger forward time - It is the time mould material is kept under pressure as it cools down and becomes rigid.
- The mould closed time whilst the product cooled down.
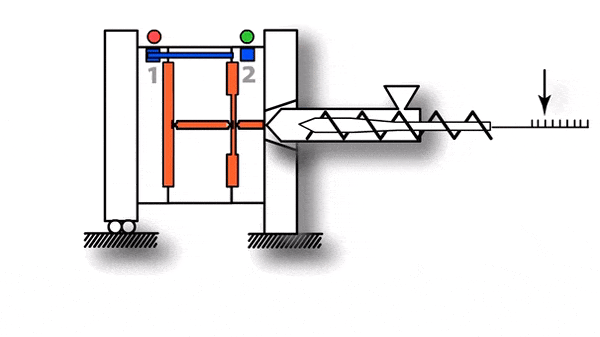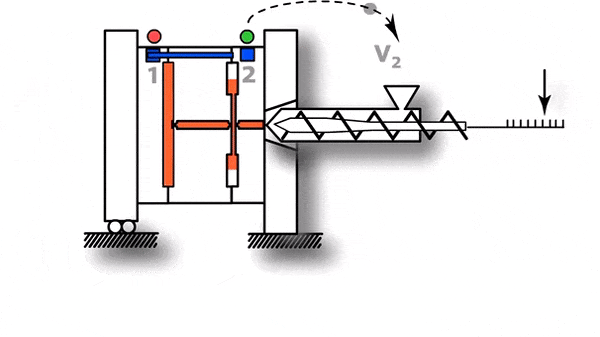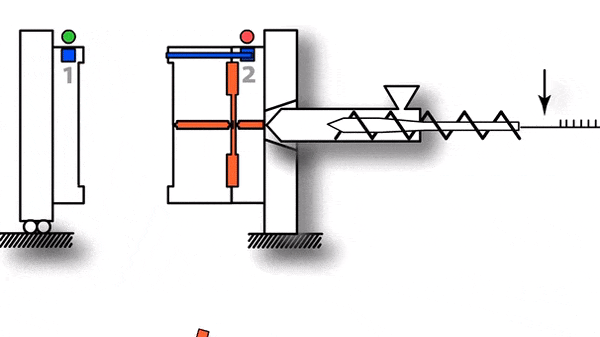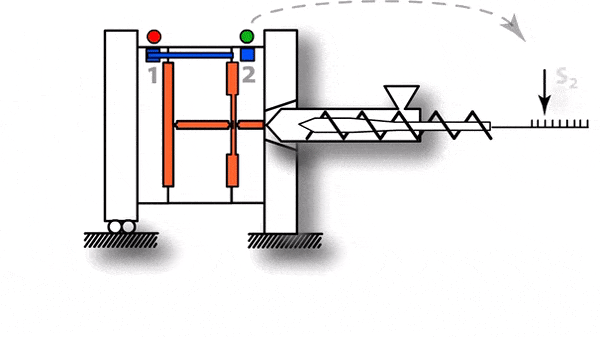
- The mould clamping force that holds two parts of mould together to ensure it withstands pressure inside the moulding cavity.
- The mould open time to eject the product and clean the mould surface before starting the next cycle.